Abstract
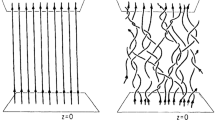
Some recent observations at Pic-du-Midi (Mulleret al., 1992a) suggest that the photospheric footpoints of coronal magnetic field lines occasionally move rapidly with typical velocities of the order 3 km s−1 for about 3 or 4 min. We argue that such occasional rapid footpoint motions could have a profound impact on the heating of the quiet corona. Qualitative estimates indicate that these occasional rapid motions can account for the entire energy flux needed to heat the quiet corona. We therefore carry out a mathematical analysis to study in detail the response of a vertical thin flux tube to photospheric footpoint motions in terms of a superposition of linear kink modes for an isothermal atmosphere. We find the resulting total energy that is asymptotically injected into an isothermal atmosphere (i.e., an atmosphere without any back reflection). By using typical parameter values for fast and slow footpoint motions, we show that, even if the footpoints spend only 2.5% of the time undergoing rapid motions, still these rapid motions could be more efficient in transporting energy to the corona than the slow motions that take place most of the time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belcher, J. W. and Davis, L.: 1971,J. Geophys. Res. 76, 3534.
Berger, M. A.: 1991, in E. R. Priest and A. W. Hood (ed.),Advances in Solar System MHD, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p. 241.
Choudhuri, A. R.: 1986, in A. I. Poland (ed.),Coronal and Prominence Plasmas, NASA Conf. Publ. 2442, p. 451.
Choudhuri, A. R.: 1990,Astron. Astrophys. 239, 335.
Dunn, R. B. and Zirker, J. B.: 1973,Solar Phys. 33, 281.
Heyvaerts, J. and Priest, E. R.: 1983,Astron. Astrophys. 117, 220.
Heyvaerts, J. and Priest, E. R.: 1984,Astron. Astrophys. 137, 63.
Heyvaerts, J. and Priest, E. R.: 1992,Astron. Astrophys., in press.
Hollweg, J. V.: 1981,Solar Phys. 70, 25.
Hollweg, J. V.: 1982,Astrophys. J. 257, 345.
Hollweg, J. V.: 1984,Astrophys. J. 277, 392.
Hollweg, J. V.: 1987,Astrophys. J. 312, 880.
Hollweg, J. V.: 1990,Computer Phys. Rep. 122, 205.
Hollweg, J. V. and Stirling, A.: 1988,Astrophys. J. 327, 950.
Koutchmy, S. and Stellmacher, G.: 1987, in E. Schröter (ed.),The Role of Fine-Scale Magnetic Fields on the Structure of Solar Atmosphere, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p. 103.
Lamb, H.: 1932,Hydrodynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Lou, Y. Q. and Rosner, R.: 1986,Astrophys. J. 309, 874.
Mehltretter, J. P.: 1974,Solar Phys. 38, 43.
Muller, R.: 1975,Solar Phys. 45, 105.
Muller, R.: 1990, ‘Solar Photosphere: Structure, Convection and Magnetic Fields’,IAU Symp. 138, 85.
Muller, R., Roudier, T., Vigneau, J., and Auffret, H.: 1992a,Proper Motions of Network Bright Points (submitted).
Muller, R., Auffret, H., Roudier, T., Vigneau, J., Simon, G., Frank, Z., Shine, R., and Title, A.: 1992b,Nature (submitted).
Osterbrock, D. E.: 1961,Astrophys. J. 134, 347.
Parker, E. N.: 1972,Astrophys. J. 174, 499.
Parker, E. N.: 1983,Astrophys. J. 264, 642.
Parker, E. N.: 1986, in A. I. Poland (ed.),Coronal and Prominence Plasmas, NASA Conf. Publ. 2442, p. 9.
Rae, I. C. and Roberts, B.: 1982,Astrophys. J. 256, 761.
Roberts, B.: 1985, in E. R. Priest (ed.),Solar System Magnetic Fields, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, p. 37.
Rosner, R., Golub, L., Coppi, B., and Vaiana, G.: 1978,Astrophys. J. 222, 317.
Ryutov, D. A. and Ryutova, M. P.: 1976,Soviet Phys. 43, 491.
Similon, P. L. and Sudan, R. N.: 1989,Astrophys. J. 336, 442.
Simon, G. W., Title, A., Topoka, K., Tarbell, T., Shine, R., Ferguson, S., Zirin, H., and SOUP Team: 1988,Astrophys. J. 327, 964.
Spruit, H. C.: 1981,Astron. Astrophys. 98, 155.
Spruit, H. C.: 1984, in S. L. Keil (ed.),Small Scale Dynamic Processes in Quiet Solar Atmosphere, National Solar Observatory, Sunspot, NM, p. 249.
Title, A. M., Tarbell, T., Topka, K., Ferguson, S., Shine, R., and SOUP Team: 1989,Astrophys. J. 336, 475.
Title, A. M., Shine, R. A., Tarbell, T. D., Topka, K. P., and Sharmer, G. B.: 1990, ‘Solar Photosphere: Structure, Convection and Magnetic Fields’,IAU Symp. 138, 49.
Ulmschneider, P., Priest, E. R., and Rosner, R.: 1991,Mechanics of Chromospheric and Coronal Heating, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
van Ballegooijen, A. A.: 1986,Astrophys. J. 311, 1001.
van der Luhe, O. and Dunn, R.: 1987,Astron. Astrophys. 177, 165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhuri, A.R., Auffret, H. & Priest, E.R. Implications of rapid footpoint motions of photospheric flux tubes for coronal heating. Sol Phys 143, 49–68 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619096
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619096